
According to a recent study, men who are at risk for heart disease may get dementia up to ten years before women who are at the same risk.
The influence of cardiovascular disease on dementia in men a decade before the females is not known before, said lead study author Dr. Paul Edison, professor of neuroscience at Imperial College London, told CNN. This is novel finding with significant health implications.
According to the World Health Organization, heart disease has been the top cause of fatalities in the US for over a century, and cardiovascular illnesses are the world’s leading cause of death.
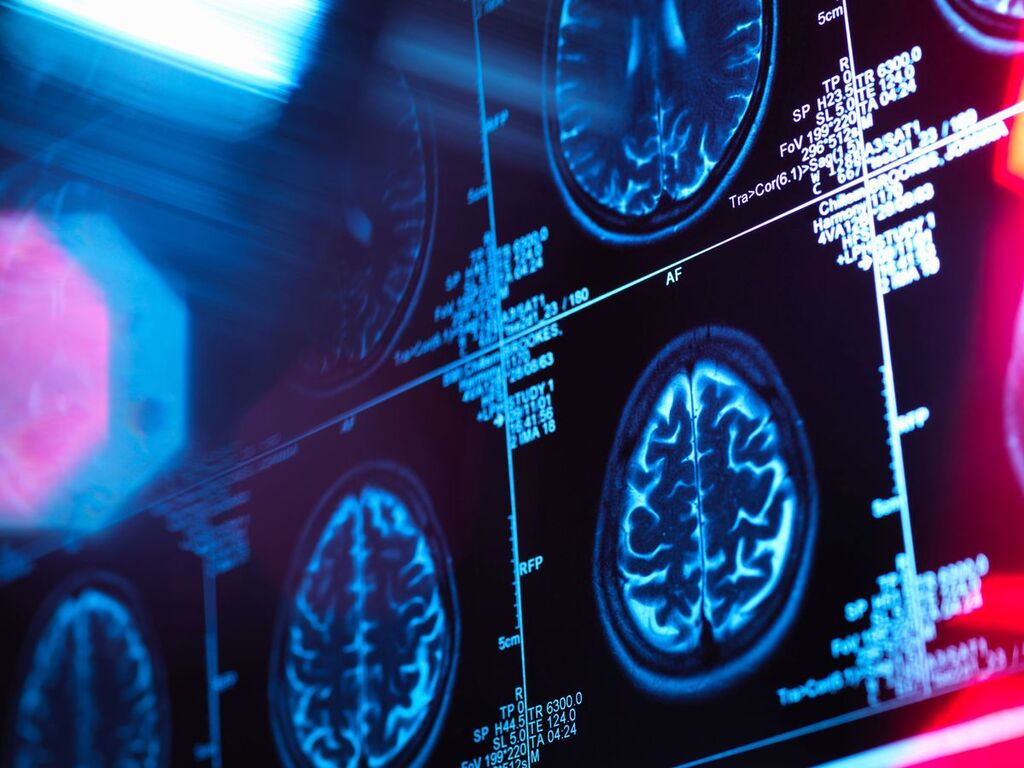
According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, heart disease risk factors include smoking, excessive alcohol use, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, obesity, and inadequate sleep and exercise. The transport of oxygen to the brain may be impacted by small vessel disease, which can result from any of several disorders.
According to the study, the detrimental effects of cardiovascular risk were equally noticeable in individuals without the APOE 4 gene as in those who did. For individuals over 65, the APOE 4 gene is thought to be the most significant risk factor for the eventual onset of Alzheimer’s disease. According to scientists, keeping a healthy lifestyle may be crucial because having one or even two copies of the gene does not ensure that Alzheimer’s will develop.
Modifying cardiovascular risk may prevent Alzheimers disease, said Edison, who is also the head of the Memory Research Centre at Imperial College London. Our results suggest that this should be done a decade earlier in males than in females irrespective of whether they carry the risk genes (APOE 4) for Alzheimers disease.
Epidemiologist Jingkai Wei, an assistant professor of family medicine at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, told CNN that the study’s results are in line with previous research that indicates increased cardiovascular risk may be linked to detrimental neurocognitive outcomes.

Wei, who was not involved in the new study, conducted similar research and discovered that poor performance on cognitive tests that measure executive function, processing speed, and immediate and delayed memory in men and women over 60 was associated with ten years of living with cardiac risk.
Click here to follow the Mirror US on Google News to stay up to date with all the latest news, sports and entertainment stories
The new study’s findings support his own, indicating that “poorer cardiovascular health is associated with both poorer cognitive function and brain pathology, which are both predictive of dementia,” Wei stated.
The study, which was published in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, examined information on almost 34,000 men and women between the ages of 45 and 82 who gave brain and abdomen scans to the UK Biobank, a UK-based longitudinal health study.
DAILY NEWSLETTER: Sign up here to get the latest news and updates from the Mirror US straight to your inbox with our FREE newsletter.
A neuroimaging procedure known as voxel-based morphometry, or VBM, was also performed on a few patients in order to determine the impact of visceral and abdominal fatwhich envelops the body’s organson brain neurodegeneration.





